 Model Architecture
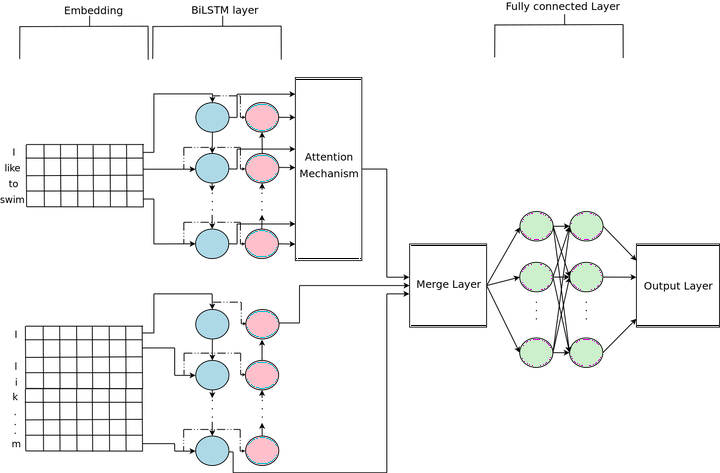
Model Architecture
Abstract
Sentiment analysis or recognizing emotions from short and noisy text from social networks such as twitter has been a challenging task. Most of the existing models use word level embeddings for the final classification of the sentiments. This paper proposes a novel representation of short text derived from a combination of word embeddings and character embeddings using Bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM). Along with this, we use attention mechanism that learns to focus on sentiment specific words. Robust representation of short text can be applied for sentiment classification as well as predicting intensity of sentiments. This paper presents evaluation of proposed model on classification as well as regression dataset. Results show significant improvement in results as compared to baselines of respective datasets.