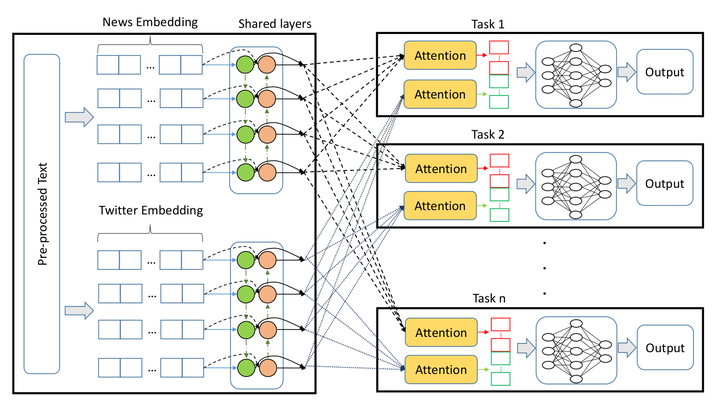
 System Architecture
System Architecture
Abstract
Most of the existing state of the art sentiment classification techniques involve the use of pre-trained embeddings. This paper postulates a generalized representation that collates training on multiple datasets using a Multi-task learning framework. We incorporate publicly available, pre-trained embeddings with Bidirectional LSTM’s to develop the multi-task model. We validate the representations on an independent test Irony dataset that can contain several sentiments within each sample, with an arbitrary distribution. Our experiments show a significant improvement in results as compared to the available baselines for individual datasets on which independent models are trained. Results also suggest superior performance of the representations generated over Irony dataset.